LEGO-Inspired Space Bricks: Pioneering the Next Era of Lunar Architecture
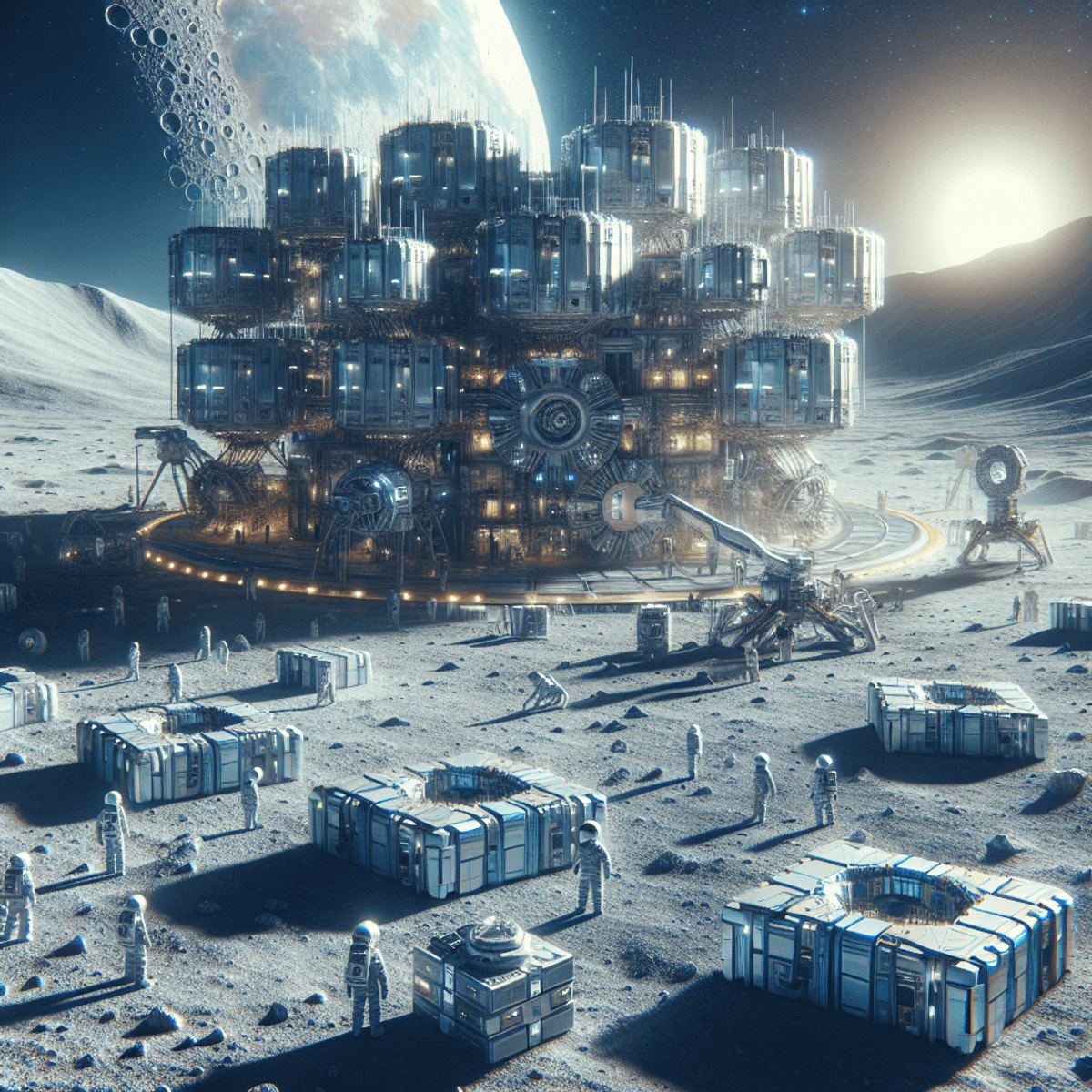
Ever dreamt of building a home on the moon? Imagine using LEGO-inspired space bricks to create lunar habitats! These innovative bricks, developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), are set to transform lunar construction. Think of it as playing with LEGO blocks but on a much grander, cosmic scale.
Why is this significant? Using sustainable materials for building on the moon isn't just smart—it’s essential. Shipping traditional construction materials from Earth is costly and impractical. Instead, ESA is focusing on utilizing local resources. They aim to use what's already there: lunar regolith, a fine, dusty soil covering the moon’s surface.
Here's where ESA’s creativity shines. By turning lunar regolith into durable space bricks, they pave the way for future moon colonies. This approach not only minimizes transportation costs but also enhances self-sufficiency in space missions.
"Using what we have to build where we are"—that's ESA's mantra for lunar architecture.
The LEGO-inspired design ensures these bricks are easy to assemble and incredibly stable. So, whether you're an astronaut or an engineer, constructing your lunar habitat just got a whole lot easier and more exciting.
The Vision for Lunar Construction
Establishing permanent structures on the moon isn't just a sci-fi fantasy, it’s a stepping stone for humanity's future in space. These lunar bases could serve as launching pads for deeper space exploration, scientific research hubs, or even tourist destinations in the cosmos.
Historical Context
The dream of lunar construction has roots tracing back to the 1960s Apollo missions. These early explorations sparked our imaginations and laid the groundwork for today's space engineering marvels. The lessons learned from those missions inform current efforts, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Challenges
Building on the moon is no small feat. The moon's environment presents unique hurdles like extreme temperatures swinging from -173°C at night to 127°C during the day. Additionally, its low gravity—about one-sixth of Earth's—demands innovative solutions to ensure structural stability and human safety.
Despite these challenges, each step forward brings us closer to turning these visions into reality.
Harnessing Local Materials: The Key to Sustainable Construction
Lunar regolith is essentially the moon’s version of soil, a loose mixture of dust, broken rock, and tiny fragments from meteorite impacts. Unlike Earth’s soil, it lacks organic material but is rich in minerals like silicon, aluminum, and iron oxide. This makes it an excellent candidate for construction materials on the lunar surface.
Using lunar regolith as a primary building material offers multiple benefits:
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Transporting materials from Earth to the moon is incredibly expensive. Utilizing local resources means fewer shipments from Earth, drastically lowering costs.
- Increased Self-Sufficiency: By using what's already available on the moon, future lunar colonies can become more self-reliant. This minimizes dependency on Earth and allows for quicker adaptation to unexpected challenges.
Resource utilization on the moon isn’t just about convenience; it’s about survival and efficiency. Imagine being able to 3D-print a building using the ground beneath your feet—that's the promise of sustainable construction with lunar regolith. This approach not only brings down logistical hurdles but also sets a precedent for off-world living that prioritizes sustainability and innovation.
Innovative Solutions: Meteorite Dust as a Resource for Space Bricks
ESA scientists have embarked on an exciting journey by creating synthetic lunar regolith from meteorite dust. This dust, collected from our solar system's history, closely mimics the composition of actual lunar soil. Imagine using ancient space debris to build the future of lunar habitats!
The Magic of 3D Printing
The real game-changer here is 3D printing technology. This tech isn't just for making funky art pieces; it’s a cornerstone for rapid prototyping and customization in space architecture. Here’s how it works:
- Creating Synthetic Regolith: ESA mixes meteorite dust with binding agents to produce a material that behaves like lunar soil.
- 3D Printing Process: This synthetic regolith is then fed into specialized 3D printers designed to operate in lunar conditions. These printers layer the material precisely to form solid, interlocking bricks.
This method allows for quick adaptation and personalization in construction projects, essential when dealing with the moon's unpredictable environment. Whether it's building a small research outpost or a large habitat, 3D printing offers flexibility and efficiency that's hard to beat.
By using both meteorite dust and advanced technology, ESA is paving the way for sustainable construction on the moon.
Designing with LEGO-Inspired Space Bricks: Modular Creativity in Lunar Architecture
Imagine the joy of snapping together LEGO bricks to create something unique. ESA's space bricks bring that same spirit to lunar construction. These LEGO-inspired space bricks feature interlocking mechanisms, making them stable and easy to assemble. The design mimics the simple yet effective functionality of our favorite childhood toy, turning lunar architecture into a giant, cosmic playset.
Modular design is at the heart of this innovation.
- Stability and Ease of Assembly: The interlocking nature ensures that structures remain sturdy even in the moon's low-gravity environment.
- Experimentation and Adaptability: Modular design allows for flexibility. Builders can experiment with different configurations, adapting quickly to new challenges or needs.
"These bricks are not just building blocks; they are stepping stones for human creativity on the moon."
Using these creative construction techniques, future astronauts can build habitats that are not only functional but also customizable. They can adapt their living spaces as requirements change, paving the way for sustainable lunar living.
The potential of LEGO-inspired space bricks goes beyond just creating shelters. It opens up endless possibilities for scientific labs, observation posts, and even recreational areas on the moon, all built through the power of modular design.
Encouraging Future Generations to Think Beyond Earth: The Role of Public Engagement Initiatives in Lunar Architecture Education
Imagine walking into a LEGO store and stumbling upon a display that instantly transports you to the moon. ESA is making this vision a reality by showcasing their innovative space bricks at select LEGO stores worldwide. This initiative aims to spark curiosity and ignite passion for science and engineering among children.
Inspiring Future Engineers
- LEGO Stores Showcase: By partnering with LEGO, ESA leverages the universal appeal of these iconic toys to introduce complex scientific concepts in an accessible manner.
- Interactive Displays: Kids can explore how these space bricks work, understand their interlocking mechanisms, and even get hands-on experience assembling structures designed for lunar habitats.
- Educational Programs: Some stores offer workshops where children can learn about lunar regolith, the challenges of space construction, and the technology behind 3D printing.
Building Interest from an Early Age
Engaging children through public engagement initiatives like this not only makes learning fun but also lays the foundation for future careers in STEM fields. These programs demystify advanced engineering projects and show that anyone with an interest in building, creativity, or space could play a part in humanity’s next giant leap.
The excitement generated by these showcases goes beyond just fun; it's about planting seeds of inspiration that could grow into the engineers, scientists, and astronauts of tomorrow. Through such tangible experiences, ESA hopes to cultivate a new generation that's ready to think beyond Earth and tackle the challenges of lunar living.
Key Takeaways from ESA's Space Brick Initiative: Paving the Way Towards Sustainable Habitats on the Moon and Beyond!
Key Points to Remember:
- Sustainable Habitats on the Moon: ESA's space brick initiative is a groundbreaking step towards creating eco-friendly, long-lasting structures using local lunar materials.
- Future Lunar Homes: By leveraging these innovative building techniques, future missions can focus on establishing permanent human habitats beyond Earth, reducing reliance on Earth-based resources.
- Impact on Space Missions: This approach not only paves the way for sustainable living on the moon but also sets a precedent for construction practices in other extraterrestrial environments.
Conclusion: Imagining Possibilities in Lunar Living with Innovative Materials like Space Bricks!
Living on the moon could soon be more than just a sci-fi dream. Think of habitats built with LEGO-inspired space bricks, designed for easy assembly and sustainability using local materials. These innovations open up fascinating prospects:
- Self-sustaining communities: Reduced dependency on Earth by harnessing lunar regolith.
- Modular designs: Adaptable and expandable living spaces catering to needs and changes.
- Resource efficiency: Lower transportation costs, leveraging in-situ resources.
This vision paves the way for future moon colonies, transforming how we think about living beyond Earth.
Listen to Majestic Truth Podcast for More Insights into Science & Exploration Topics!
If you're interested in space and innovative ideas like LEGO-inspired space bricks, you should check out the Majestic Truth Podcast. We discuss the latest news, explore new theories, and analyze advanced technologies. Our episodes are designed to ignite curiosity and motivate future explorers.



Leave a comment